Are you overwhelmed by mounting debt? Feeling trapped by high-interest rates and struggling to make ends meet? You’re not alone. Millions of Americans grapple with the burden of multiple debts, from credit cards and medical bills to personal loans and student loans. This article explores debt consolidation, a powerful financial tool that can help you simplify your finances and potentially save you money. We’ll delve into how debt consolidation works, its benefits and drawbacks, and help you determine if it’s the right solution for your financial situation.
Understanding debt consolidation is crucial for anyone looking to gain control of their finances. This process involves combining multiple debts into a single, new loan. By streamlining your payments into one monthly installment, you can simplify your budget and potentially lower your overall interest rate. We will examine the different debt consolidation methods available, including balance transfer credit cards, personal loans, and debt management programs, so you can choose the strategy that best suits your individual needs and credit score. Learn how debt consolidation can help you regain financial stability and pave the way toward a brighter financial future.
What Is Debt Consolidation?
Debt consolidation is a financial strategy designed to simplify and potentially streamline your debt repayment process. It involves taking out a new loan—often a lower-interest loan—to pay off multiple existing debts, such as credit cards, personal loans, or medical bills.
The primary goal of debt consolidation is to reduce the overall cost of borrowing by lowering your interest rate. Many individuals find themselves juggling multiple debts with varying interest rates and minimum payments, making it difficult to manage and potentially leading to higher overall interest payments. Debt consolidation aims to consolidate these debts into a single, more manageable payment.
There are several methods for consolidating debt, including personal loans, balance transfer credit cards, and home equity loans. Each method has its own advantages and disadvantages, such as interest rates, fees, and eligibility requirements. Choosing the right method depends heavily on your individual financial situation and creditworthiness.
Understanding the implications of debt consolidation is crucial before proceeding. While it can offer significant benefits, such as simplified repayment and potentially lower interest rates, it’s important to carefully consider the terms of the new loan and ensure that it aligns with your financial goals. Failure to do so could lead to further financial difficulties.
It’s important to note that debt consolidation doesn’t magically erase debt. It simply changes how you manage and repay it. Responsible budgeting and financial planning are still essential for successful debt consolidation.
When It Makes Sense to Consolidate
Debt consolidation can be a powerful tool for managing your finances, but it’s not always the right solution. It makes the most sense when you’re dealing with multiple high-interest debts, such as credit card debt and personal loans. By consolidating these debts into a single loan with a lower interest rate, you can significantly reduce your monthly payments and pay off your debt faster.
Another scenario where consolidation shines is when you’re struggling to keep track of multiple due dates and payment amounts. A single, consolidated loan simplifies your financial management, making it easier to stay organized and avoid late payments. This streamlined approach can also reduce the stress associated with managing numerous accounts.
Consolidation can also be beneficial if you have a history of missed payments or poor credit. While a lower interest rate isn’t guaranteed, a consolidated loan can give you a chance to rebuild your credit score by consistently making on-time payments. This demonstrates responsibility to lenders and can eventually lead to improved financial opportunities.
However, it’s crucial to remember that consolidation isn’t a magic bullet. It’s essential to carefully consider the terms of the consolidated loan, ensuring the interest rate is genuinely lower than your existing debts and that the loan term is manageable. Failure to do so could extend your repayment period and ultimately increase the total interest paid.
Finally, consider the fees associated with the consolidation process. Some loans carry significant origination fees or prepayment penalties, which can offset any savings gained from a lower interest rate. A thorough comparison of all fees and interest rates is vital before making a decision.
Types: Loans vs Balance Transfers
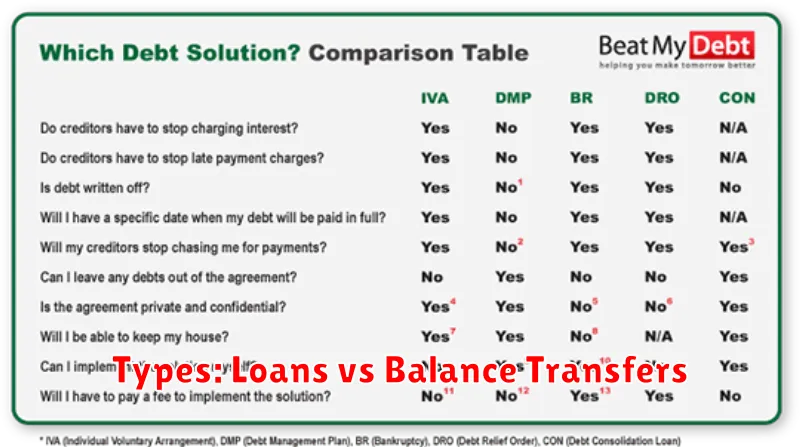
Debt consolidation involves combining multiple debts into a single, more manageable payment. There are two primary types of debt consolidation: loans and balance transfers.
A debt consolidation loan is a new loan you take out to pay off your existing debts. This loan can be secured (backed by collateral, like a house or car) or unsecured (not backed by collateral). The interest rate on a consolidation loan will depend on your credit score and the lender’s terms. Once you receive the loan, you use the funds to pay off your credit cards, personal loans, or other debts. You then make a single monthly payment to the lender.
A balance transfer involves moving your existing debt from one credit card to another, often one with a lower interest rate (a balance transfer credit card). This strategy can save you money on interest if you can pay off the balance before the introductory period ends. However, balance transfer cards often charge fees, and it’s crucial to understand the terms and conditions carefully. Failing to pay off the balance within the promotional period can result in a high interest rate being applied retroactively.
The best type of debt consolidation for you depends on your individual financial circumstances. Consider factors such as your credit score, the amount of debt you owe, and your ability to make timely payments. It’s often beneficial to compare offers from multiple lenders before making a decision.
Impact on Credit Score
Debt consolidation can have a significant impact on your credit score, but the effect isn’t always positive. The outcome depends heavily on how you manage the process and your existing credit profile.
Positive Impacts: One potential benefit is a reduction in your credit utilization ratio. This ratio compares your total credit card debt to your total available credit. By consolidating high balances onto a single loan, you may lower this ratio, leading to a credit score improvement. Furthermore, if you successfully repay your consolidated debt on time, this demonstrates responsible credit management, boosting your score.
Negative Impacts: However, the process can also negatively affect your score. Applying for multiple loans during the consolidation process will result in multiple hard inquiries on your credit report, each temporarily lowering your score. Additionally, opening a new line of credit, such as a personal loan used for consolidation, can momentarily reduce your average credit age, which can slightly lower your score. Finally, failure to repay the consolidated debt on time will severely damage your credit history, leading to a significant drop in your score.
Overall: The overall impact on your credit score depends on various factors including your existing credit history, the type of consolidation method chosen, and your ability to manage the new debt responsibly. While consolidation can potentially improve your score, it’s crucial to carefully consider the potential risks before proceeding.
Things to Check Before Applying
Before you apply for a debt consolidation loan or program, it’s crucial to carefully assess your financial situation and understand the implications. Taking this preliminary step can save you from potential pitfalls and ensure you choose the right option.
First, calculate your total debt. This includes credit cards, personal loans, medical bills, and any other outstanding balances. A clear understanding of your overall debt burden is essential for determining the feasibility of consolidation and for selecting a suitable loan amount.
Next, compare interest rates from different lenders. Debt consolidation isn’t always beneficial if the new interest rate is higher than your existing rates. Shop around and compare offers to find the most competitive rate possible. Be sure to consider both the Annual Percentage Rate (APR) and any associated fees.
It’s also important to check your credit score. A higher credit score typically qualifies you for better interest rates and loan terms. Review your credit report for any errors and take steps to improve your score before applying, if necessary. A strong credit history will significantly impact your approval chances and the terms you receive.
Finally, understand the terms and conditions of the loan thoroughly. Pay close attention to the repayment period, fees, and any penalties for late payments. Avoid loans with hidden fees or unfavorable terms. Ensure the loan terms align with your financial capabilities and repayment plan.
Alternatives to Consider
Before diving into debt consolidation, it’s crucial to explore alternative solutions that might better suit your financial situation. These alternatives can potentially offer lower costs and less risk than consolidation.
One viable option is to create a budget and aggressively tackle your highest-interest debts first using the debt avalanche method. This strategy focuses on minimizing the total interest paid by prioritizing high-interest debts, even if the minimum payments on other debts remain unchanged. This requires discipline and a strong commitment to your financial plan.
Another approach involves negotiating with your creditors directly. Many creditors are willing to work with borrowers experiencing financial hardship. You might be able to negotiate lower interest rates, reduced monthly payments, or even a settlement for less than the total amount owed. This requires strong communication skills and a clear understanding of your financial situation.
For individuals facing overwhelming debt and struggling to manage payments, credit counseling can prove invaluable. Nonprofit credit counseling agencies offer free or low-cost guidance on debt management strategies, including developing a budget, negotiating with creditors, and exploring debt management plans (DMPs). A DMP consolidates your payments into one monthly payment, often at a reduced interest rate.
Finally, consider seeking professional financial advice from a certified financial planner or other qualified advisor. They can assess your specific financial circumstances and recommend the most appropriate course of action, taking into account your income, expenses, and debt levels. Personalized guidance can be invaluable in making informed decisions about your debt.

